
|
Please note: Some links on Traum Homestead are Amazon links. As an Amazon Associate, we earn a small commission for sending you to Amazon. It costs you NOTHING extra. These links look like this. Your support through these links helps sustain the content and journey we share here. Thank you for being an integral part of Traum Homestead!
What is USDA Zone?
USDA Zones, also known as Plant Hardiness Zones, are defined regions based on the average annual minimum winter temperature. They help gardeners and farmers determine which plants are most likely to thrive in their local climate. For homesteaders, understanding USDA Zones is crucial for selecting the right crops and planning planting schedules.
|
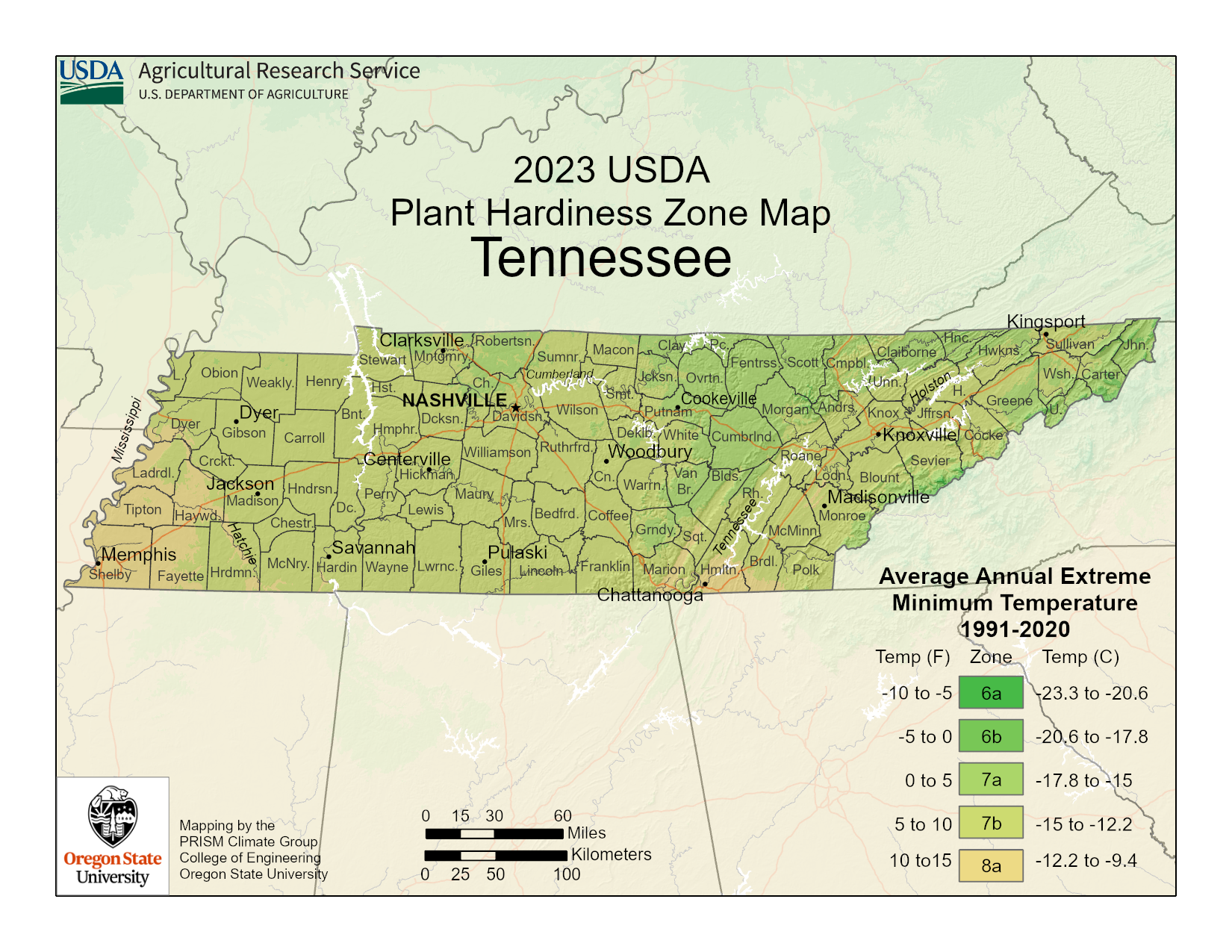
USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, 2023. Agricultural Research Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture. Accessed from https://planthardiness.ars.usda.gov/
How it works:
USDA zones are geographic areas defined by their minimum winter temperature, ranging from Zone 1 (coldest) to Zone 13 (warmest). Each zone representing a 10-degree difference in that areas lowest winter temperature.
Half-Zones:
Each zone is broken down into half-zones with a classification of either (a) or (b). Each one representing a 5 degree difference in extreme minimum temperature.
Why is USDA Zone Important?
Knowing your USDA Zone helps you choose perrenial plants that are well-suited to your climate, increasing your chances of successful harvests. This knowledge can prevent crop failures due to unsuitable weather conditions. For example, a homesteader in Zone 5 can avoid planting things like rosemary in the ground, or fig trees. There are a wide range of plants that would not survive a Zone 5 winter. According to the USDA, using zones can significantly improve agricultural outcomes.
How to Implement USDA Zone on Your Homestead
Implementing USDA Zone knowledge on your homestead involves several steps:
Step 1: Identify Your USDA Zone
Use online tools like the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map or consult local agricultural extensions to determine your zone.
Step 2: Research Suitable Plants
Identify which plants thrive in your zone. Many seed catalogs and gardening resources list plants by USDA Zone suitability.
Step 3: Plan Your Garden Layout
Design your garden layout according to zone-specific guidelines, ensuring each plant has the optimal conditions.
Step 4: Adjust Planting Schedules
Adapt your planting schedules based on zone recommendations, planting cold-hardy crops earlier and tender crops later in the season.
Step 5: Monitor and Adapt
Pay attention to seasonal variations and microclimates on your property. Adjust your practices accordingly to optimize plant growth.
Troubleshooting USDA Zone Common Issues
Even with careful planning, you may encounter issues. Here are some common problems and solutions:
Unexpected Weather Changes
Protect plants with frost blankets, row covers, cold frames, or greenhouses.
Microclimate Effects
Utilize areas with unique conditions (e.g., a south-facing brick wall) to extend growing seasons.
Frost Damage
Plant frost-tolerant varieties and use mulch to insulate roots.
FAQs
You probably still have some lingering questions. Below we have addressed some of the most frequently asked questions to help fill in any gaps. Reviewing these FAQ’s will give you a deeper insight into some of the key aspects covered. If you still have questions feel free to let us know in the comment section below!
How do I determine my USDA Zone?
Use online tools such as the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map or consult local agricultural extensions.
Can I grow plants not recommended for my USDA Zone?
Yes, these plants will absolutely need extra protection when the temperature dips down below what that individual plant can withstand. These plants should be in containers, and brought into a warmer area like a greenhouse, or indoors.
How do USDA Zones affect livestock and animal husbandry?
Zones influence the types of forage crops you can grow for fodder and the timing of breeding cycles of the livestock. Certain breeds can withstand the colder temperatures than others. Ensure that you do your do diligence and find the right breed for your area.
Conclusion
Additional Resources
United States Department of Agriculture: How to Use the Maps - A more in depth guide to understanding and using the USDA Hardiness Zone Maps for gardening.
Better Homes & Gardens: How to Use Plant Hardiness Zones to Decide What to Grow - An in-depth article on choosing plants based on USDA Zones.
Gardening Know How Gardening By Zone - Tips and tricks for homesteading success in different USDA Zones.

 Digital Products (Etsy)
Digital Products (Etsy)
 Apparel
Apparel
 Memberships
Memberships
 Courses (Coming Soon!)
Courses (Coming Soon!)
 Shop All
Shop All





No comments:
Post a Comment
What do you think?